Why do I need to use White-UICSS?
White-UICSS helps you to build fast, responsive sites. It is Powerful and extensible. It is easy to set up and master, it has a good grid system, styling for many HTML elements ranging from typography to buttons, as well as support of JavaScript plugins, making it even more flexible.
Every front-end developer’s goal is to create a multi functioning, easy-to-navigate, and aesthetically appealing front-end design for website and web/mobile apps. It might seem very basic, but the effort that goes into building such a front-end requires a lot of patience, efforts such as writing repetitive and time-consuming coding processes. Fortunately, a team of developers started to build a Framework that lightened the burden on the shoulders of front-end developers, and they named it White-UICSS.
White-UICSS is a powerful framework that has taken web development, especially front-end development, and community to the next level. Also, it paces up the development process by offering resources such as templates and themes, which can be customized according to the project needs. Moreover, it’s an open-source framework, and you can modify it without spending a penny.
What makes White-UICSS different from other CSS FrameWorks?
White-UICSS is time saving: When you are bound to an extremely confined timeline to build a website, web app or mobile app, you can use White-UICSS and nail your project effortlessly. It’s because of the ready-made blocks built ready for you to use them. Clearly, you don’t have to start everything from scratch, and you can modify certain elements to make it unique with your inputs.
White-UICSS also unpacks ready-made themes & templates when you add it to your project. You can choose from it, or you can also opt to include inputs from other sources. But, you must also be aware that there are a lot of people who do the same. Hence, to look unique from the rest of the websites that have the same theme or template, you need to get a little creative and tweak certain things so that it defines your website or application distinctively.
- White-UICSS is easy to use: Maybe you are an expert or a beginner in web technologies, you can swiftly do the White-UICSS installation for yourself without any hassle. As said, though you don’t have to be an expert in web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), having basic knowledge of them don’t hurt.
- White-UICSS has responsive grid systems: Creating a page starts from creating a grid layout for your page. Responsive grid systems are of utmost priority as there is an increase in the usage of smartphones. Any disorientation in front-end design will directly impact on the authenticity of the website and your website fails to gain the visitors’ trust. Since White-UICSS has been built under the idea of Mobile-First, its grid system can divide the screen into 12 equal columns and accommodate the elements according to the screen size. This makes your website’s front-end mobile-friendly. Also, with the help of the grid system’s classes, you can hide and show certain elements only on certain devices.
White-UICSS is customizable: You can always tweak the CSS file if you’re not satisfied with White-UICSS’s design template. Also, you can combine it with your existing design and make them complement each other’s functions. It is very much helpful when you want to give your website a distinct look, but you don’t have enough time to learn or code custom CSS from scratch.
With the help of White-UICSS’s customization page, you can tweak it further to create your own theme. Also, you must identify and remove all the plugins and components that you will not require for your web project. Moreover, you also get to have a section where you can customize your template by changing the values to the variables.
- White-UICSS is compatible with all browsers: The White-UICSS team ensures the compatibility of the framework with all modern browsers versions and platforms. Also, the team claims that they don’t support all proxy browsers and older browsers, but that doesn’t affect its display or functionality.
- White-UICSS establish consistency: For a longer period, there have been inconsistencies prevailing between the Front-end and Backend development teams. The creators of White-UICSS wanted to find a solution to establish consistency among them. Thus, they came up with White-UICSS that eradicates the use of libraries that differ from developer to developer. Hence, no matter who handles the project, the framework establishes consistency throughout the project. Since it is also cross-browser compatible, no matter what browser you use for your development purpose, it consistently reflects the same output across all browsers.
- White-UICSS is an open source: Since White-UICSS is an open-source framework, you can modify according to your project demands without having to spend a dime on licenses. Also, it encourages the fellow community developers to contribute so that it can grow at a steady pace.
How can I use White-UICSS?
Below is how you can use White-UICSS in your HTML document:
Include White-UICSS’s production-ready CSS and JavaScript via CDN without the need for any build steps.
- Create a new
index.htmlfile in your project root. Include the <meta name="viewport> tag as well for proper responsive behavior in mobile devices.
Code Sample:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>White-UICSS demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
</body>
</html>
- Include White-UICSS’s CSS and JS. Place the
<link>tag in the<head>for our CSS, and the<script>tag for our JavaScript bundle before the closing</body>tag.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>White-UICSS demo</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/white-uicss@1.0.3/white-uicss.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/white-uicss@1.0.3/white-uicss.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Why do script tags sometimes appear in the body instead of the head?
The best method is to put JavaScript(JS) <script> tags just before the closing </body> tag, rather than in the <head> section of your HTML. The reason for this is that HTML loads from top to bottom. The head loads first, then the body, and then everything inside the body.
Here's what happens when a browser loads a website with a <script> tag on it:
Fetch the HTML page (e.g.
index.html)Begin parsing the HTML
The parser encounters a
<script>tag referencing an external script file.The browser requests the script file. Meanwhile, the parser blocks and stops parsing the other HTML on your page.
After some time, the script is downloaded and subsequently executed.
The parser continues parsing the rest of the HTML document.
Step #4: causes a bad user experience. Your website basically stops loading until you've downloaded all scripts. If there's one thing that users hate, it's waiting for a website to load.
Why does this even happen?
Any script can insert its own HTML via document.write() or other DOM manipulations. This implies that the parser has to wait until the script has been downloaded and executed before it can safely parse the rest of the document. After all, the script could have inserted its own HTML in the document.
However, most JavaScript developers no longer manipulate the DOM while the document is loading. Instead, they wait until the document has been loaded before modifying it. For example:
HTML
<!-- index.html -->
<html>
<head>
<title>My Page</title>
<script src="my-script.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="user-greeting">Welcome back, user</div>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript
// my-script.js
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
// this function runs when the DOM is ready, i.e. when the document has been parsed
document.getElementById("user-greeting").textContent = "Welcome back, Bart";
});
Because your browser does not know my-script.js isn't going to modify the document until it has been downloaded and executed, the parser stops parsing.
Some websites built with White-UICSS FrameWork:
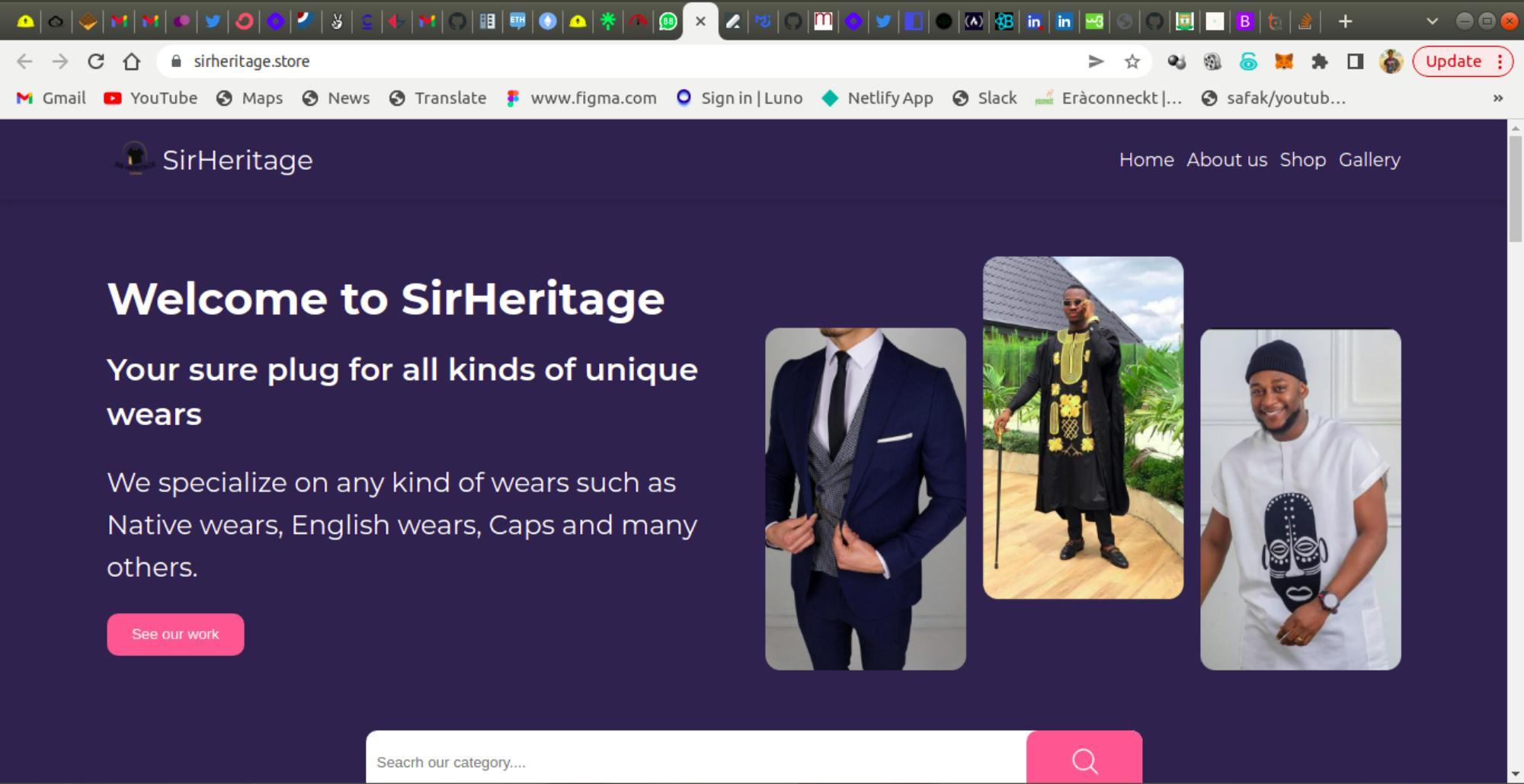
- Sirheritage Store: You can click on this link to check how beautiful this website is with White-UICSS
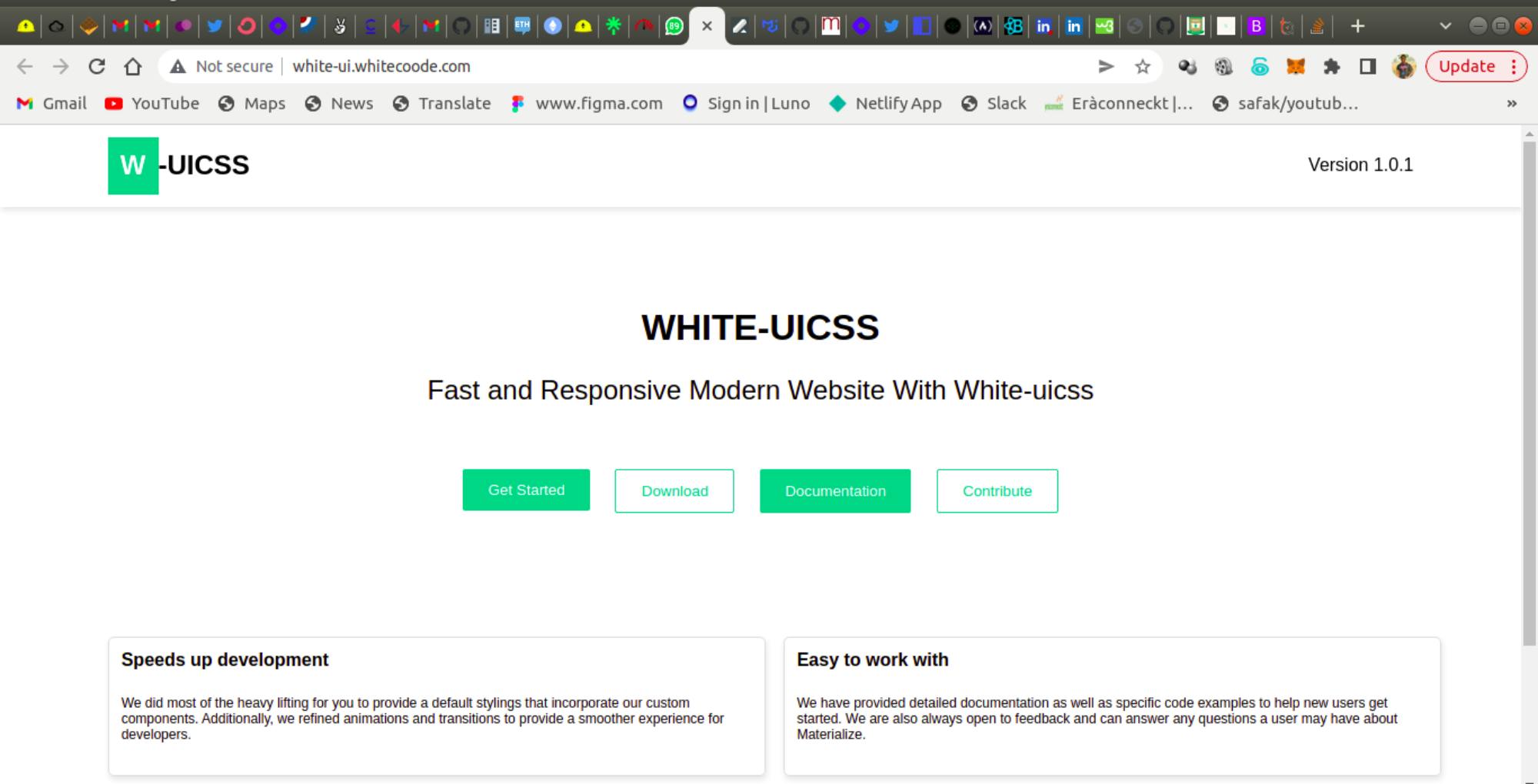
- White-UICSS: White-UICSS website was built with White-UICSS FrameWork. This is awesome. Click on this link to check it out.
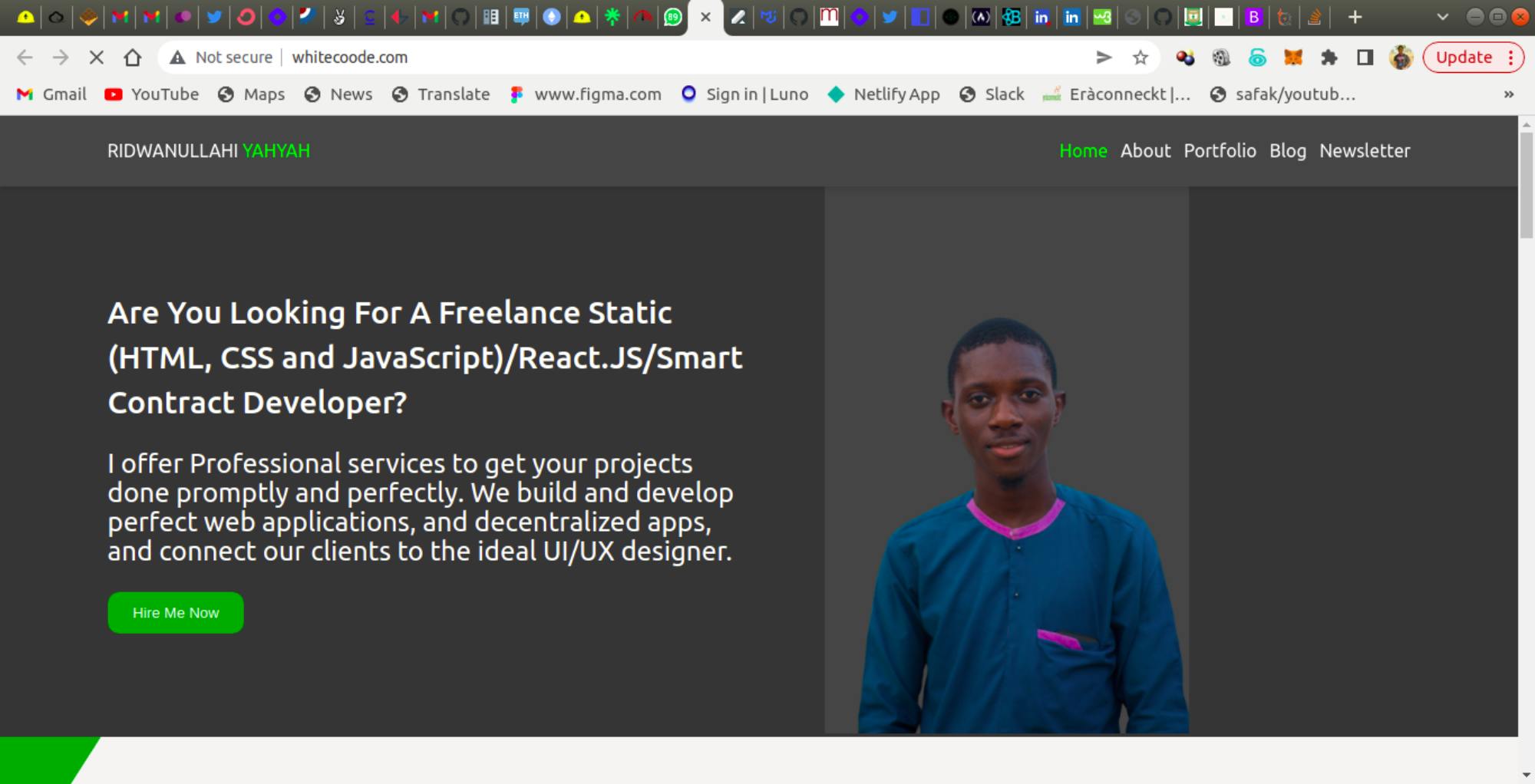
- WhiteCoode portfolio website: WhiteCoode also built his amazing portfolio using White-UICSS. Click the link to check this amazing, and beautiful UI portfolio.
Thanks for reading...
Happy Coding!
